在mysql5.0之前和之后的区别:多了一个information_schema数据库
Mysql监听端口号:3306
1、数据库服务器:
安装了数据库管理系统软件的计算机就叫数据库服务器,数据库服务器为客户提供服务,这些服务是查询、更新、事务管理、索引、高速缓存、查询优化、安全及多用户存取控制等。
2、数据库管理系统(DBMS) :
是一种操纵和管理数据库的大型软件,用于建立、使用和维护数据库。它对数据库进行统一的管理和控制,以保证数据库的安全性和完整性。
3、常见的DBMS :
1、Access:Microsoft Office Access是由微软发布的数据库管理系统 。
2、Oracle:Oracle是美国甲骨文公司的一款关系数据库管理系统,一般作为大型或超大型网站的数据库。
3、SQL Server:SQL Server 2000 是Microsoft 公司推出的SQL Server数据库管理系统。
4、MySQL:MySQL由瑞典MySQL AB公司开发,目前属于Oracle公司。Mysql是最流行的关系型数据库管理系统之一
数值类型(整型)
 数值类型(浮点型)
数值类型(浮点型)
 日期和事件类型
日期和事件类型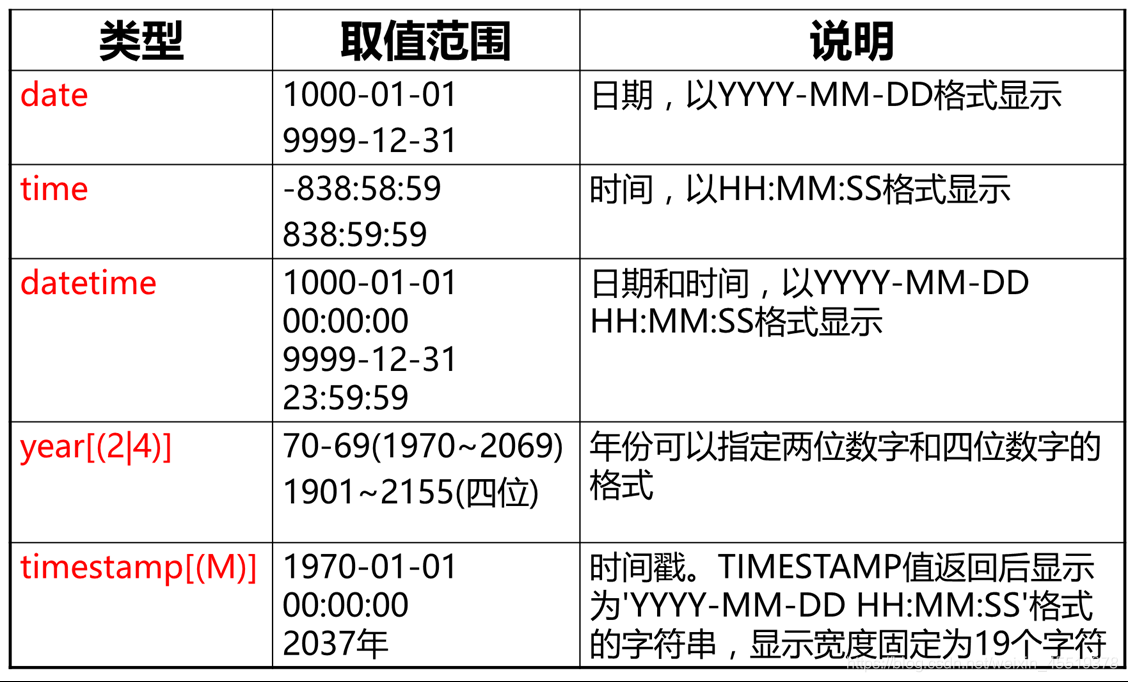
字符串类型
 Mysql基本命令(cmd)
Mysql基本命令(cmd)
1、命令行下,修改数据库默认字符集:Alter Database dbname 2、Default Character Set utf8(一般不要轻易改,排错的时候用)
3、mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -proot //进入数据库
4、mysqladmin -u用户名 -p旧密码 password 新密码 //修改密码
5、quit/exit //退出数据库
关于创建:
1、创建数据库:create databasse
2、创建数据库格式:create database [if not exists] db_name [charset 字符集]
if not exists:[If not exists]可选,如果没有指定,并且存在同名数据库,则报错。
3、创建数据表:
(1)先创建数据库 create database 表名
(2)选择数据库 :use 表名
(3)创建数据表并添加字段:create table student(id int(10) not null auto_increment primary key,name varchar(32),num int (10),score int (10));
关于增加记录:(insert into)
向数据表中插入信息:
insert into class(name,num,score) values(‘mashuqing’,201601,80);
关于查看信息:
1、select * from 表名 //查看某个数据表中的所有信息
2、select database() //查看当前数据库
3、命令行下satus : //查看当前数据
4、show databases //显示所有数据库(只能看到我拥有某些权限的数据库)
5、use 表名 //选择数据库
6、desc 表名 //查看某个数据表
关于更改数据表:
1、alter table class rename message; //更改数据表class的名字为message
2、alter table class drop num; //删除数据表中的num列
3、alter table message change name uname varchar(32); //更改数据表message里name的字符串类型的取值范围
4、alter table message modify name varchar(32); //修改message表里的name的类型
更新记录:–update set
update class set num=1,score=2;
关于select查询语句的应用:
1、select * from class where id=12 //查询主键为12的数据
2、 select * from class where id<>3; //查询id不为3的数据
3、select * from class where id>5 //查询id大于5的数据
4、 select * from class where id<10 //查询id小于10的数据
5、 select * from class where id=10 || id=12 //查询id分别为10,12的数据
6、 select * from class where name=‘mashuqing’ and num=201601; //查询name为mashuqing并且num=201601的数据
7、select * from 表名 where id in(4,6) //查询id分别为4,6的数据
8、select * from 表名 where id between 5 and10 //查询id值在5到10之间的数据
9、select * from 表名 where id not in (3,5) //查询id不为3并且不为5的数据
10、select * from 表名 where (id>=3 and id <=5 ) or (id <=10) //查询id 在3到5之间和8到10的数据
关于limit查询语句的应用:
1、select * from class limit 1; //查询第一条数据
2、select * from class limit 5,3; //从第5条开始,跳过第五条,查3条数据
对查询的记录排序(order by ):
1、select * from class(表名) order by id(字段名) asc; //对数据记录排序–升序
2、select * from class(表名) order by id(字段名) desc; //对数据记录排序–倒序
3、select * from class(表名) order by name desc,id desc; //先按照第一个字段的顺序排序,如果有重复的,再按照第二个字段排序(如果按照第一个字段排完序,没有出现重复的,那第二个字段的排序将没有意义)
4、 select * from class order by 3; //查询所有数据,3代表的是3列
模糊查询(like):
1、select * from class(表名) where name like ‘%m%’; //只要name里包含m的都会被查询出来
2、select * from class(表名) where name like ‘m_’; //比%更加精确
注:
如果要查找的字符中包含“%”或“_”或"",则只要对他们进行转义–加\就可以(select * from class where name like ‘%%%’;)
聚合函数:
max()、min()、avg()、count()、sum
1、select sum(id) from class(表名) //算出所有id的总和
2、 select avg(score) from class; //求字段score的平均数
3、 select max(score) from class group by name ; //在name里查询score最大的
分组(group by ):
1、select count() from class(表名) group by score(字段); //根据字段score将表分组,值相同的为一组,利用count进行计数(每个组中有几条数据)
2、select count() from class group by score,name; //按照字段score进行分组,然后再按照name进行分组,用count()进行计数
筛选器:–用于对已查询结果的筛选
注:1、该关键字主要用于对查询结果的再次筛选(使结果更加精确)
2、一般情况下与group by配合使用
1、select count()sex from class group by sex having sex=‘男’; //输出sex在class表里,根据组选出sex='男’的
联合查询:–用来合并两个或多个select语句的结果集
注:1、union关键字前后的select查询的字段数量要求一致
2、union会自动在查询结果中去除重复数据
1、select name,score from class where id >5 union select name,num from class; //合并两个查询结果
关于删除与更新
1、drop databases 数据库名 //删除数据库
2、delete from 表名 where id=? //删除某一条数据(一定要记得加where id=? ,不然所有的记录都会被删除!!!)
3、update 表名 set 字段名=? where id=? //更新数据表中的记录
4、truncate table :快速删除表中数据,重新设置auto_increment计数器(只删除数据,表结构还会留下,删的快)----auto_increment会从头开始计数
来源:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45519378/article/details/102757581