1.vue组件
1.1局部组件的使用
var App = { tempalte:` <div class='app'></div>` }; //2.挂子 <App />单闭合 双闭合都可以 new Vue({ el:"#app", //用子 template:<App /> components:{ App } })<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> *{ padding: 0; margin: 0; } body{ color: #fff; } .main{ width: 100%; } .head{ width: 100%; height: 70px; background-color: purple; text-align: center; font-size: 20px; line-height: 70px; } .wrap{ width: 100%; height: 1200px; } .wrap .aside{ width: 30%; height: 1200px; background-color: green; float: left; } .wrap .content{ width: 70%; height:1200px; background-color:yellowgreen; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> // 打油诗: 先声子 挂子 用子 // 1.先声明头部组件 var Vheader = { template:` <header class='head'> 我是头部 <span>{{count}}</span> <button @click = 'count+=1'>点击</button> </header> `, data(){ return { count: 0 } }, methods:{ } }; var Vaside = { template:` <div class='aside'> 我是侧边栏 </div> ` }; var Vcontent = { template:` <div class='content'> 我是内容区域 </div> ` } // 1.声明入口组件 /* 1.头部组件 2.侧边栏 3.内容组件 4.脚步组件 */ // 局部组件 我是入口组件 //<Vheader></Vheader>双闭合 //<Vaside />单闭合 var Vmain = { template:` <div class='main'> <Vheader></Vheader> <div class='wrap'> <Vaside /> <Vcontent /> </div> </div> `, components:{ // 等价于Vheader:Vheader 2.挂载子 Vheader, Vaside, Vcontent } } new Vue({ el:"#app", // 3.使用子组件 template:`<Vmain />`, //入口组件 data:{ }, components:{ // 2.挂载子组件 key表示组件名 value:组件对象 Vmain:Vmain } }); </script> </body> </html>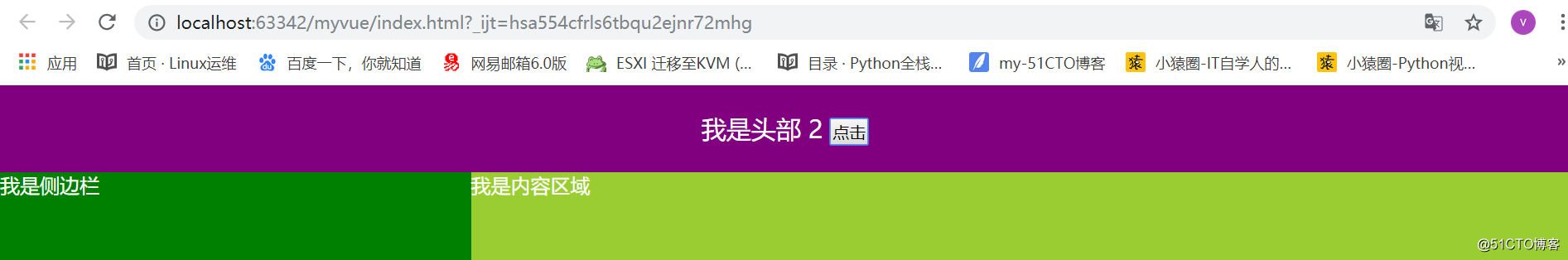
1.2父组件向子组件传递数据:通过Prop
1.在子组件自定义特性。props:['自定义的属性1','自定义属性2'] 当一个值传递给一个 prop 特性的时候,它就变成了那个组件实例的一个属性,那么我们就可以像访问data中的值一样 2.要在父组件中导入的子组件内部 绑定自定义的属性 <Vheader :title = '父组件中data声明的数据属性'/> 注意:一个组件默认可以拥有任意数量的 prop,任何值都可以传递给任何 prop。<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> *{ padding: 0; margin: 0; } body{ color: #fff; } .main{ width: 100%; } .head{ width: 100%; height: 70px; background-color: purple; text-align: center; font-size: 20px; line-height: 70px; } .wrap{ width: 100%; height: 1200px; } .wrap .aside{ width: 30%; height: 1200px; background-color: green; float: left; } .wrap .content{ width: 70%; height:1200px; background-color:yellowgreen; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> // 打油诗: 先声子 挂子 用子 // 1.先声明头部组件 var Vheader = { template:` <header class='head'> <span>{{title}}</span> <span>{{count}}</span> <button @click = 'count+=1'>点击</button> </header> `, data(){ return { count: 0 } }, props:['title'], methods:{ } }; var Vaside = { template:` <div class='aside'> 我是侧边栏 </div> ` }; //自定义组件时,使用v-for,必须要有:key = 'post.id' var Vcontent = { template:` <div class='content'> <ul> <li v-for = 'post in posts' :key = 'post.id'> <h3>我的博客标题:{{post.title}}</h3> <p>我的博客内容:{{post.content}}</p> </li> </ul> <button @click='changeSize'>改变字体大小</button> </div> `, props:['posts'], methods:{ changeSize(){ // 通过$emit()方法来触发自定义的事件 // 第一个参数是自定义的事件名字 第二个参数就是传递的值 // this指的vue实例化对象的子类 this.$emit('postChangeSize',3) } } }; var Vmain = { data(){ return{ fontsize:18 } }, template:` <div class='main' :style = '{fontSize:fontsize+"px"}'> <Vheader v-bind:title = 'title'></Vheader> <div class='wrap'> <Vaside /> <Vcontent v-bind:posts = "appPosts" @postChangeSize = 'clickHandler'/> </div> </div> `, methods:{ clickHandler(value){ this.fontsize = this.fontsize+value; } }, components:{ // 等价于Vheader:Vheader 2.挂载子 Vheader, Vaside, Vcontent }, props:['title','appPosts'] } new Vue({ el:"#app", // 3.使用子组件 template:`<Vmain :title = "text" :appPosts = "posts"/>`, data:{ text:"vita热爱学习,想要成为大牛!!加油加油gogogo!", posts:[ {id:1,title:"组件中的传值",content:"通过Prop传递数据"}, {id:2,title:"组件中的传值2",content:"通过Prop传递数据2"}, {id:3,title:"组件中的传值3",content:"通过Prop传递数据3"}, ] }, components:{ // 2.挂载子组件 key表示组件名 value:组件对象 Vmain:Vmain } }); </script> </body> </html>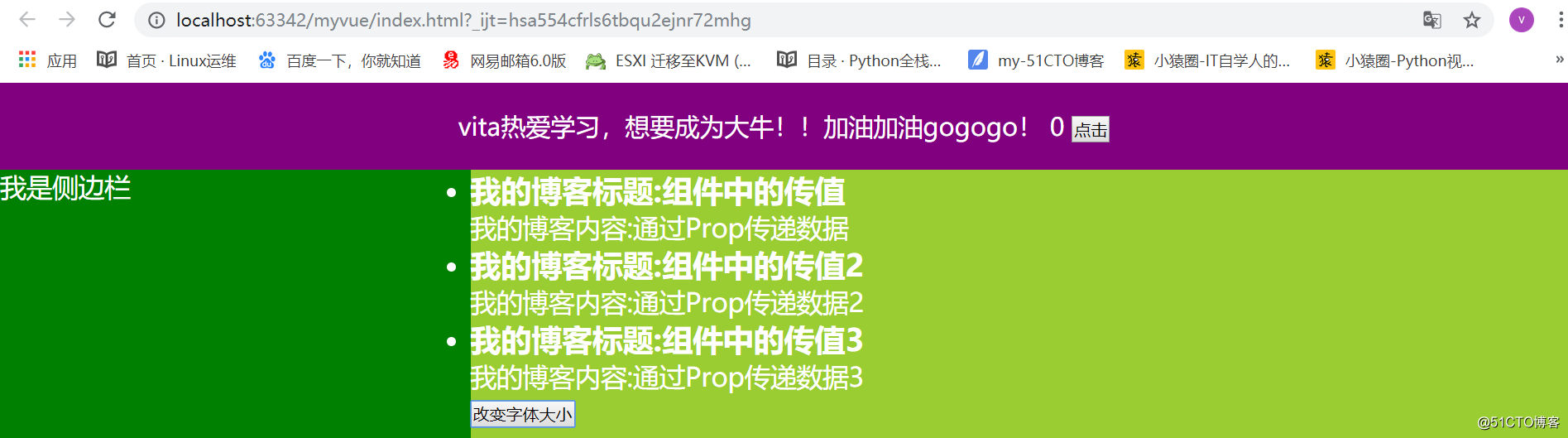
1.3子组件传递数据到父组件
1.给子组件中的某个按钮绑定原声事件,。我们可以调用内建的 this.$emit('自定义的事件名','传递的数据'),来向父级组件触发一个自定义的事件. 2.在父组件中的子组件标签中 要绑定自定义的事件, 上面的例子中,更改字体大小的按钮事件,就使用了 this.$emit1.4全局组件.slot组件
Vue.component('全局组件的名字',{ 跟new Vue() 实例化对象中的options是一样,但是要注意: 不管是公共组件还是局部组件 data必须是个函数 函数一定要返回 {} }) #slot Vue.component('Vbtn', { template: `<button class='defalut' :class='type'> <slot></slot> </button>`, props: ['type'] }); //全局组件使用的时候,不需要components:注入 var Vheader = { data() { return { } }, template: `<div id='head'> <Vbtn>登录</Vbtn> <Vbtn>注册</Vbtn> <Vbtn>提交</Vbtn> <Vbtn>默认的按钮</Vbtn> <Vbtn type='primary'>主要的按钮</Vbtn> <Vbtn type='success' >成功的按钮</Vbtn> </div>` };<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style> * { padding: 0; margin: 0; } #head { width: 100%; height: 80px; background-color: purple; } .defalut { display: inline-block; line-height: 1; white-space: nowrap; cursor: pointer; background: #fff; border: 1px solid #dcdfe6; border-color: #dcdfe6; color: #606266; text-align: center; box-sizing: border-box; outline: none; margin: 0; transition: .1s; font-weight: 500; padding: 12px 20px; font-size: 14px; border-radius: 4px; } .primary { color: #fff; background-color: #409eff; border-color: #409eff } .success { color: #fff; background-color: #67c23a; border-color: #67c23a; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> // 创建公共组件 // 第一个参数是公共组件的名字,第二个参数options Vue.component('Vbtn', { template: `<button class='defalut' :class='type'> <slot></slot> </button>`, props: ['type'] }); //全局组件使用的时候,不需要components:注入 var Vheader = { data() { return { } }, template: `<div id='head'> <Vbtn>登录</Vbtn> <Vbtn>注册</Vbtn> <Vbtn>提交</Vbtn> <Vbtn>默认的按钮</Vbtn> <Vbtn type='primary'>主要的按钮</Vbtn> <Vbtn type='success' >成功的按钮</Vbtn> </div>` }; // 局部组件的使用 var App = { template: `<div> <Vheader></Vheader> </div>`, components: { Vheader } } new Vue({ el: '#app', data() { }, template: `<App />`, components: { App } }); </script> </body> </html>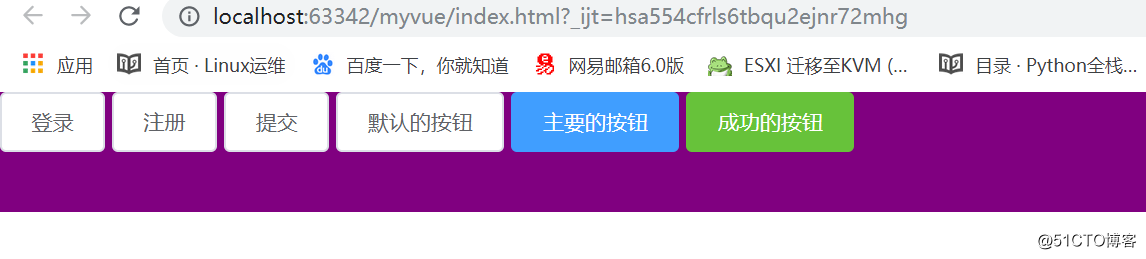
2.过滤器
###局部过滤器 //1.注册局部过滤器 在组件对象中定义 filters:{ '过滤器的名字':function(value){ } } //2.使用过滤器 使用管道符 | {{price | '过滤器的名字'}} ##### 全局过滤器 // 注册全局的过滤器 //第一个参数是过滤器的名字,第二个参数是执行的操作 Vue.filter('reverse',function(value) { return value.split('').reverse().join(''); }); //使用跟 局部过滤器一样<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> <style> </style> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model = 'price'> <h3>{{ price | currentPrice}}</h3> <h4>{{msg | reverse}}</h4> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> // 注册全局的过滤器 Vue.filter('reverse',function(value) { return value.split('').reverse().join(''); }) new Vue({ el: '#app', data() { return{ price:0, msg:"hello vita" } }, // 局部过滤器 在当前 组件中声明过滤器 filters:{ currentPrice:function (value) { // 参数1就是纯涤的元数据 console.log(value); return '$' + value; } } }); </script> </body> </html>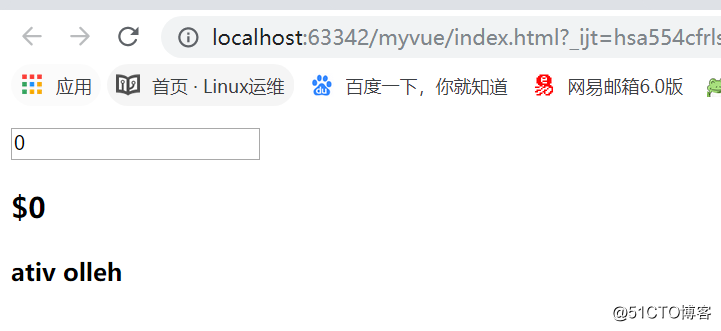
3.计算属性
3.1侦听多个属性:计算属性watch
侦听的是单个属性 watch:{ 数据属性的名字:function(value){ }, 数据属性的名字2:function(value){ } }<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model='myName'> <h3>{{ myName}}</h3> <button @click='clickHandler'>修改</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> new Vue({ el:'#app', template:``, data(){ return { myName:'', firtName:'VV' } }, methods:{ clickHandler(){ this.myName = 'vita'; } }, watch:{ // 检测单个属性 命令式 myName:function(value) { console.log(value); if (value === 'vita') { console.log(value +' '+this.firtName+'爱学习,想要成为大牛,加油gogogogogogo!!!') } } } }); </script> </body> </html>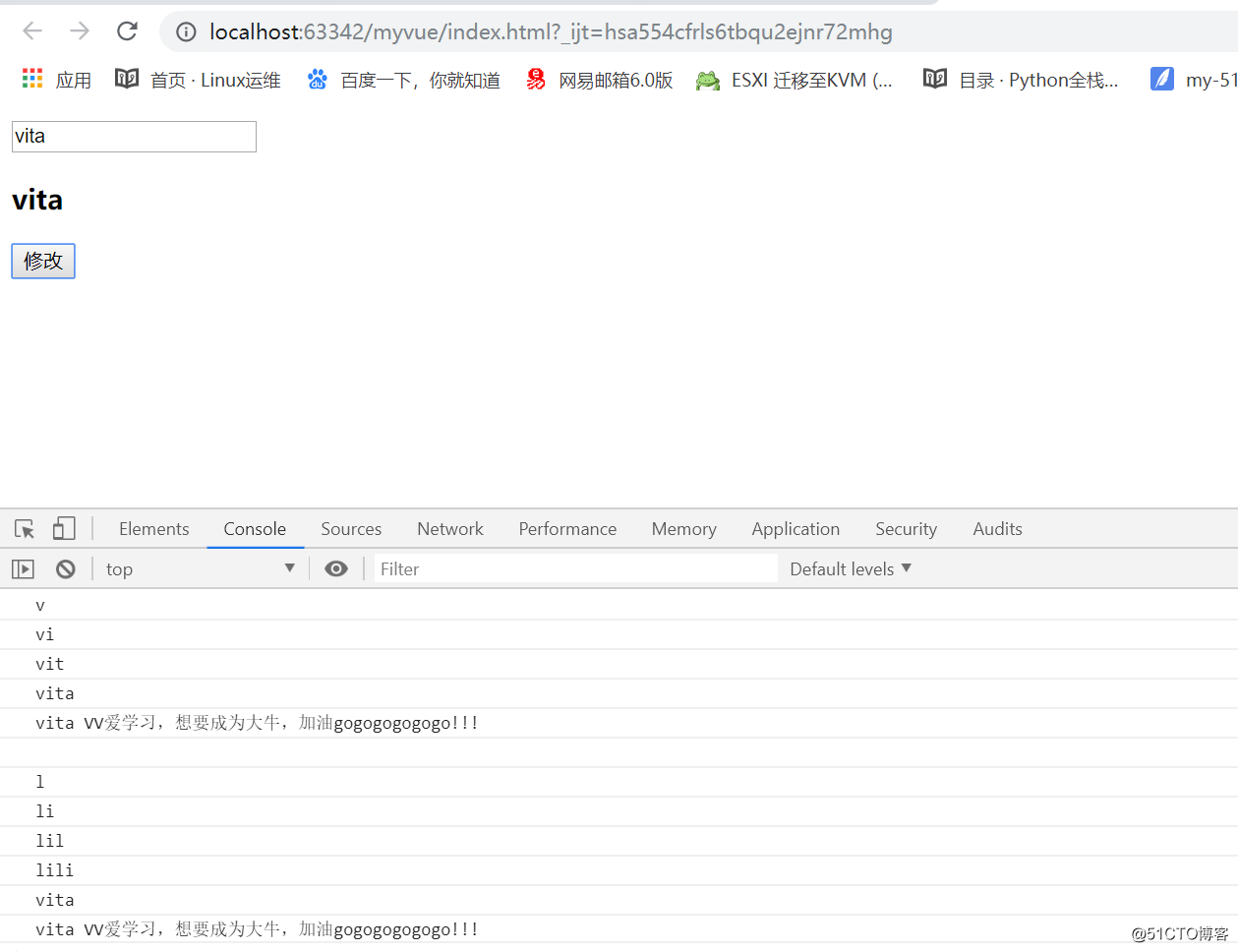
3.2侦听多个属性:计算属性 computed
计算属性 :默认只有getter方法 compuetd:{ key:value 计算属性的方法名:funtion(){ return ${this.name}他的年龄是${this.age} } }<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h4>{{vitaDesc}}</h4> <button @click='clickHandler'>修改</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> new Vue({ el:'#app', template:``, data(){ return { myName:'vita', age:18 } }, methods:{ clickHandler(){ this.myName = 'VITA'; this.age = 28; } }, computed:{ vitaDesc:function() { var str = `${this.myName}它的年龄是${this.age},努力成为大牛,加油加油,gogogo!`; // 默认只有getter return str; } } }); </script> </body> </html>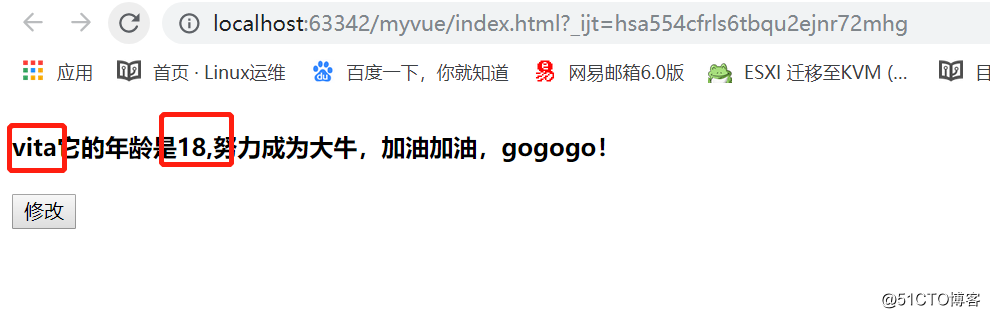
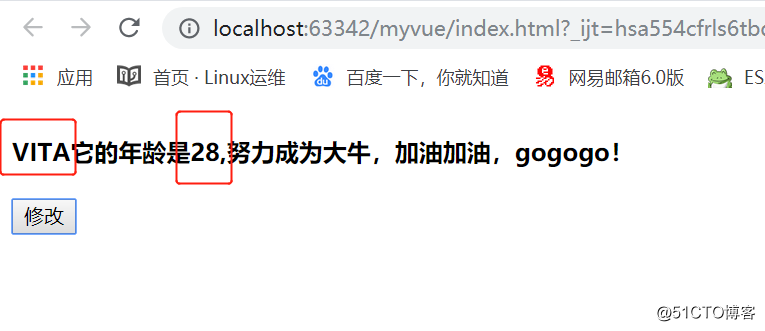
3.3计算属性的setter方法
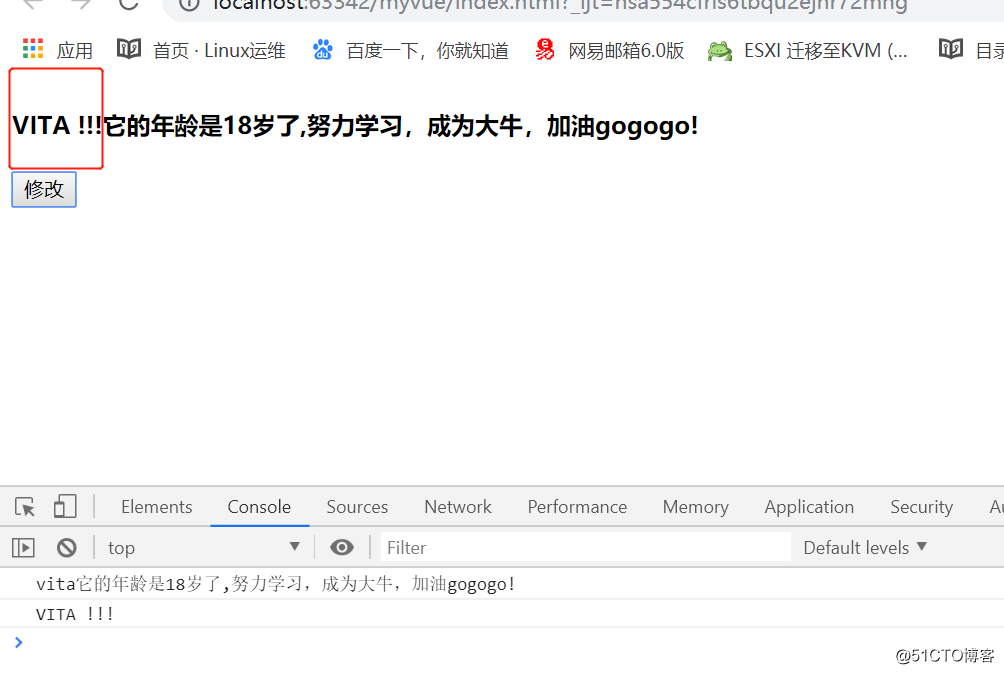
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <h4>{{vitaDesc}}</h4> <button @click='clickHandler'>修改</button> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> new Vue({ el:'#app', template:``, data(){ return { myName:'vita', age:18 } }, methods:{ clickHandler(){ console.log(this.vitaDesc); this.vitaDesc = 'VITA !!!'; } }, computed:{ vitaDesc:{ set:function(newValue) { console.log(newValue); this.myName = newValue; }, get:function() { var str = `${this.myName}它的年龄是${this.age}岁了,努力学习,成为大牛,加油gogogo!`; // 默认只有getter return str; } } } }); </script> </body> </html>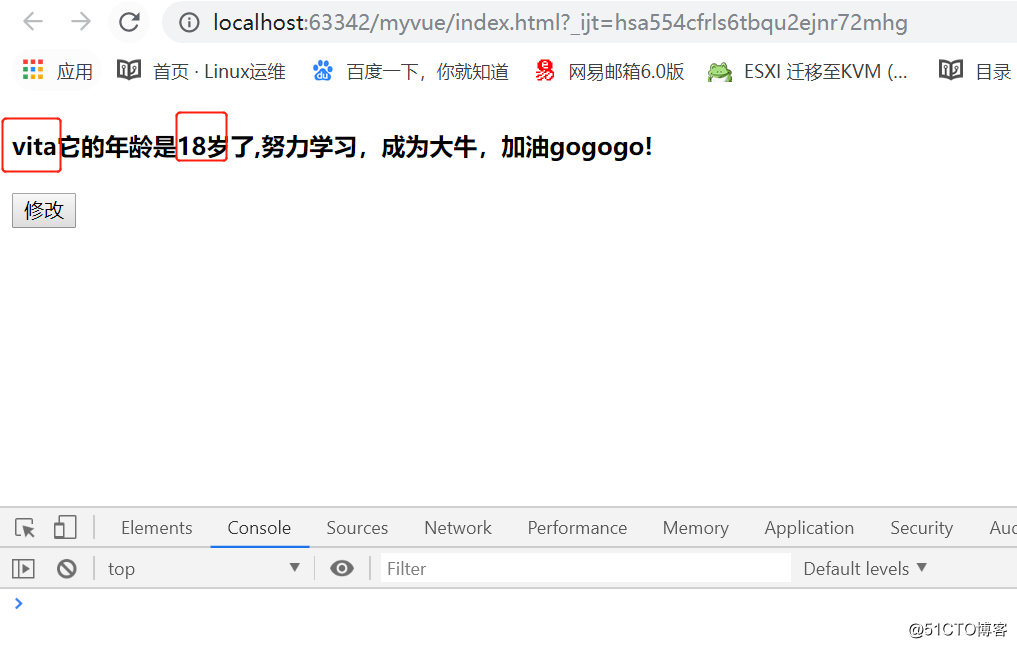
3.4setter的用途
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title></title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <input type="text" v-model = 'alexDesc'> <h4>{{alexDesc}}</h4> <!-- <button @click='clickHandler'>修改</button> --> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> new Vue({ el:'#app', template:``, data(){ return { myName:'', } }, computed:{ alexDesc:{ set:function(newValue) { this.myName = newValue; }, get:function() { return this.myName; } } } }); </script> </body> </html>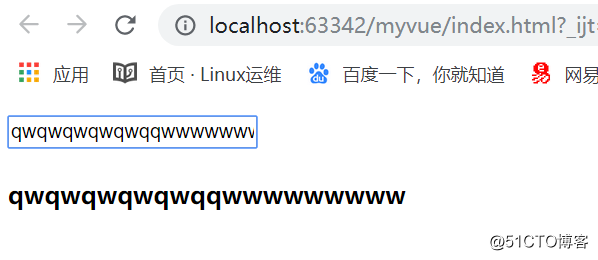
3.5计算属性之音乐播放器
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title></title> <style type="text/css"> *{ padding: 0; margin: 0; } ul{ list-style: none; } ul li { margin: 30px 20px; padding: 10px; } ul li.active{ background-color: #20FFFF; } </style> </head> <body> <div id="music"> <audio :src="currentSrc" controls autoplay></audio> <ul> <li v-for = '(item,index) in musics' @click = 'clickHandler(index)' :class = '{active:currentIndex == index}'> <h2>{{item.id}}--歌曲为:{{item.name}}</h2> <p>歌手:{{item.author}}</p> </li> </ul> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> var musicData = [{ id: 1, name: '于荣光 - 少林英雄', author: '于荣光', songSrc: './static/于荣光 - 少林英雄.mp3' }, { id: 2, name: 'Joel Adams - Please Dont Go', author: 'Joel Adams', songSrc: './static/Joel Adams - Please Dont Go.mp3' }, { id: 3, name: 'MKJ - Time', author: 'MKJ', songSrc: './static/MKJ - Time.mp3' }, { id: 4, name: 'Russ - Psycho (Pt. 2)', author: 'Russ', songSrc: './static/Russ - Psycho (Pt. 2).mp3' } ]; new Vue({ el: '#music', data() { return { musics:musicData, currentIndex:0 // musicSrc:'./static/于荣光 - 少林英雄.mp3' } }, methods:{ clickHandler(index){ // alert(index); this.currentIndex = index; } }, computed:{ currentSrc(){ // 监听了两个属性 musics currentIndex return this.musics[this.currentIndex].songSrc; } }, template: `` }); </script> </body> </html>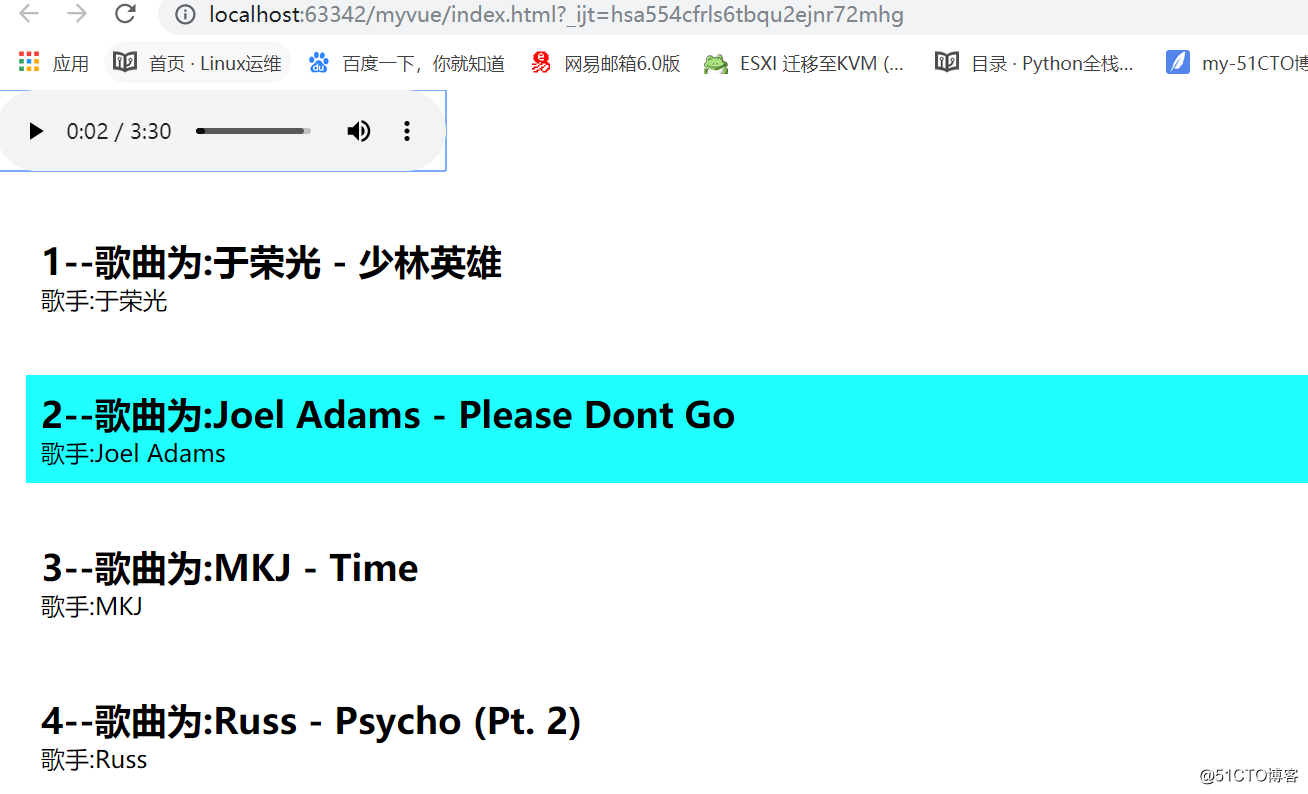
4.生命周期
4.1生命周期的方法
https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/instance.html#%E7%94%9F%E5%91%BD%E5%91%A8%E6%9C%9F%E5%9B%BE%E7%A4%BA<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"> <App></App> </div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> // 钩子函数 // beforeCreate // created // beforeMount // mounted // beforeUpdate // updated // activated // deactivated // beforeDestroy // destroyed // 创建 销毁 var Test = { data(){ return{ msg:"哈哈哈" } }, template:` <div> <div>{{msg}}</div> <button @click = 'changeHandler'>修改</button> </div> `, methods:{ changeHandler(){ this.msg = this.msg + 'vita' } }, beforeCreate(){ // 组件创建之前 console.log("beforeCreate-----------", this.msg); }, created(){ // 组件创建之后 // 使用该组件,就会触发以上的钩子函数,created中可以操作数据,发送ajax,并且可以实现vue==》页面的影响 应用:发送ajax请求 console.log("created-----------", this.msg); // this.msg = '嘿嘿黑'; }, beforeMount(){ // 装载数据到DOM之前会调用 console.log("beforeMount-----------", document.getElementById('app')); }, mounted(){ // 这个地方可以操作DOM // 装载数据到DOM之后会调用 可以获取到真实存在的DOM元素,vue操作以后的DOM console.log("mounted-----------", document.getElementById('app')); }, beforeUpdate(){ // 在更新之前,调用此钩子,应用:获取原始的DOM console.log("beforeUpdate-----------", document.getElementById('app').innerHTML); }, updated(){ // 在更新之前,调用此钩子,应用:获取最新的DOM console.log("updated-----------", document.getElementById('app').innerHTML); }, //由于性能问题,我们都不会使用消除组件和创建组件的方式,而是使用is-show的方式 beforeDestroy(){ console.log("beforeDestroy-----------", 'beforeDestroy'); }, destroyed(){ console.log("destroyed-----------", 'destroyed'); }, // activated(){ console.log("activated-----------", '组件被激活了'); }, deactivated(){ console.log("deactivated-----------", '组件被停用了'); } } var App = { data(){ return { isShow : true } }, //<keep-alive>让当前的组件产生缓存,提高前端的性能 template:` <div> <keep-alive> <Test v-if = 'isShow'></Test> </keep-alive> <button @click = 'changeHandler'>改变组件的生死</button> </div> `, methods:{ changeHandler(){ this.isShow = !this.isShow; } }, components:{ Test } } new Vue({ el:'#app', template:``, components:{ App } }); </script> </body> </html>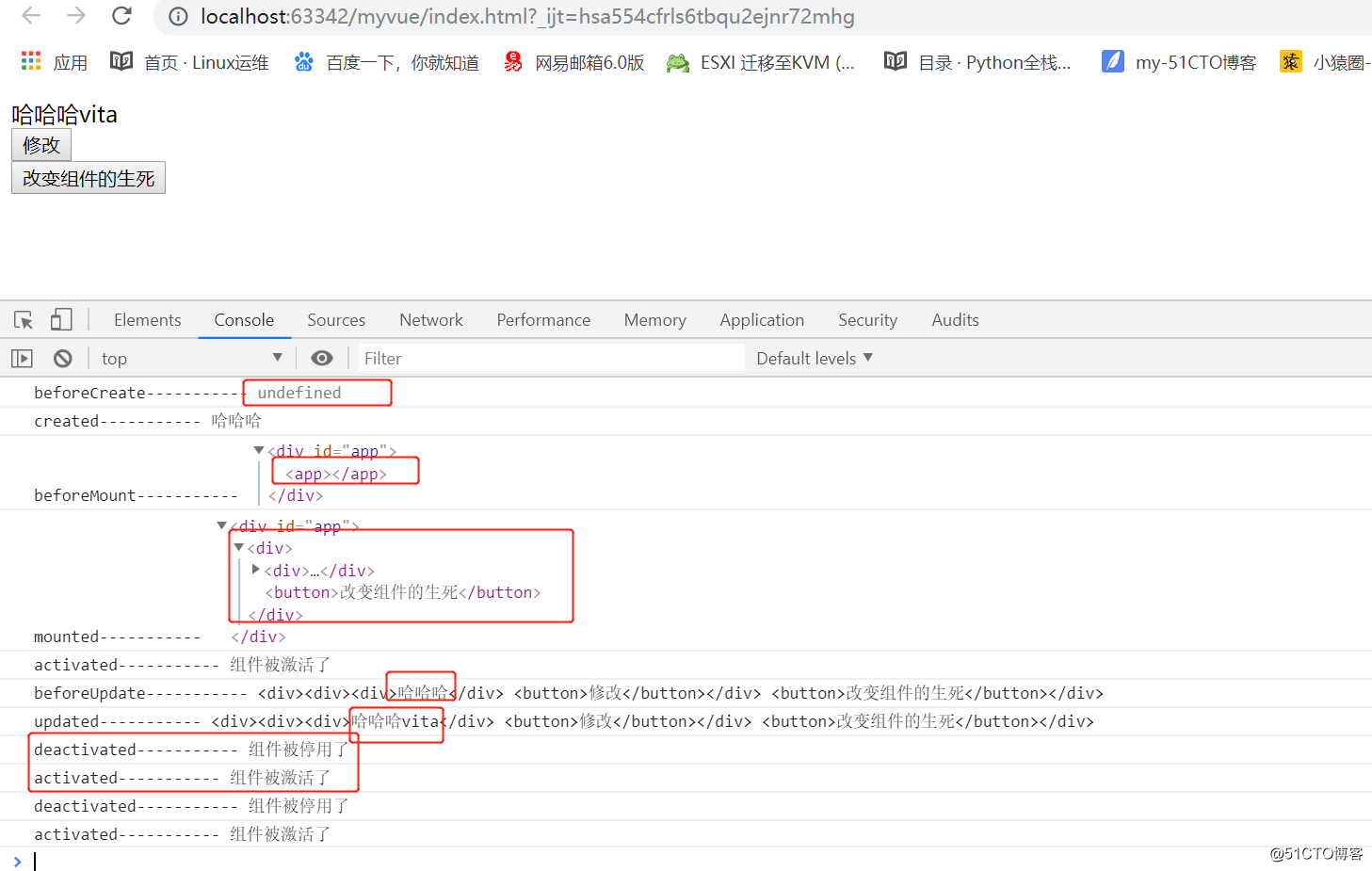
4.2使用$refs获取DOM元素
// $属性: // $refs获取组件内的元素 // $parent:获取当前组件的父组件 // $children:获取当前组件的子组件 // $root:获取New Vue的实例化对象 //$el:获取组件对象的DOM元素<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"></div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> Vue.component('subComp',{ template:`<div></div>` }) var App = { template: `<div> <subComp ref = 'subc'></subComp> <button ref = 'btn'>我是按钮</button> <p ref = 'sb'>vita</p> </div>`, beforeCreate() { console.log(this.$refs.btn);//undefined }, created() { console.log(this.$refs.btn);//undefined }, beforeMount() { console.log(this.$refs.btn); //undefined }, mounted() { console.log("this----------",this); console.log("this.$refs.btn取到的是DOM对象----------",this.$refs.btn); // 如果是给组件绑定的ref = 'subc'属性那么this.$refs.subc取到的是组件对象 console.log("this.$refs.subc取到的是组件对象----------",this.$refs.subc); var op = this.$refs.sb; this.$refs.btn.onclick = function() { console.log("op.innerHTML", op.innerHTML); } } } new Vue({ el: '#app', data() { return { } }, template: `<App />`, components: { App } }); </script> </body> </html>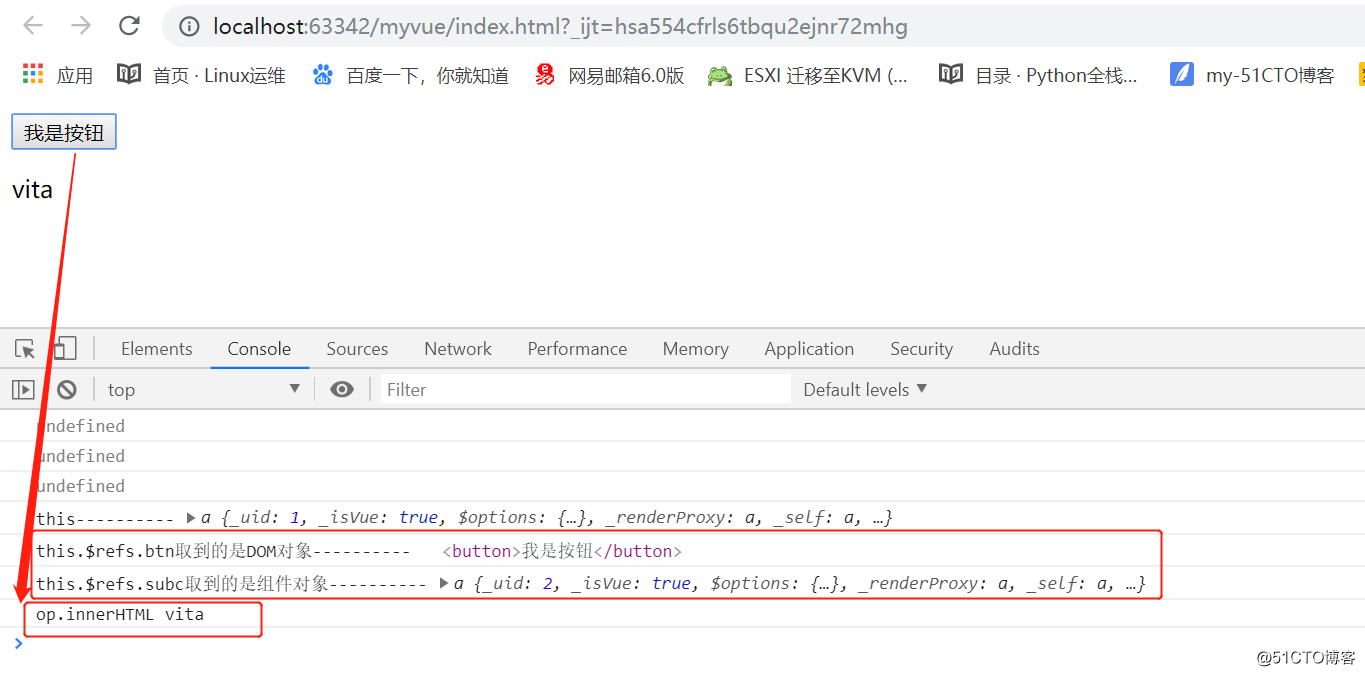
4.3使用$nextTick的特殊情况
获取更新之后的dom添加事件的特殊情况 nextTick 是在下次Dom更新循环结束之后执行的延迟回调,在修改数据之后使用$nextTick ,则可以在回调中获取更新之后的DOM <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> </head> <body> <div id="app"></div> <script type="text/javascript" src="./node_modules/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script> <script type="text/javascript"> var App = { data(){ return{ isShow:false } }, template: `<div> <input type="text" v-if = 'isShow' ref = 'fos'/> </div>`, mounted() { // vue实现响应式并不是数据发生变化之后DOM立刻发生变化,而是按一定的策略进行DOM的更新 //更新DOM this.isShow = true; //这里是获取不到DOM元素的,不能设置focus() console.log( this.$refs.fos); // $nextTick 是在下次Dom更新循环结束之后执行的延迟回调,在修改数据之后使用$nextTick ,则可以在回调中获取更新之后的DOM this.$nextTick(function() { // 获取更新之后的DOM this.$refs.fos.focus() }); } } new Vue({ el: '#app', data() { return { } }, template: `<App />`, components: { App } }); </script> </body> </html>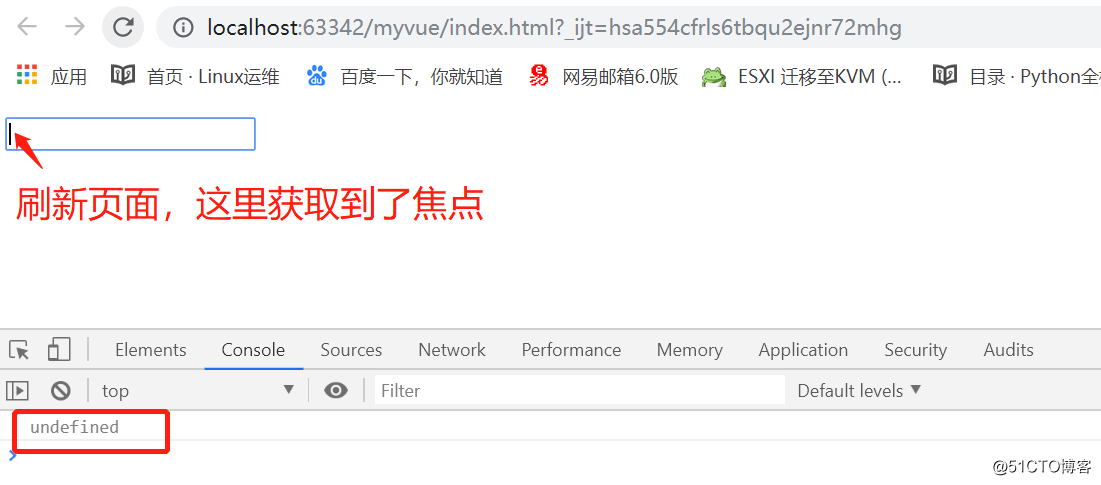
来源:51CTO
作者:DevOperater
链接:https://blog.51cto.com/10983441/2434436