import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import h5py import scipy from PIL import Image from scipy import ndimage % matplotlib inline 第一部分: python 的numpy 基础练习
1.1“sigmoid ”
def sigmoid(x): """ 计算x的sigmoid 参数: x 是一个值 或者一个数列,范围是无穷 返回: s -- simoid(x) """ s = 1.0/(1+1/np.exp(x)) return s - 测试当x是一个值或者一个数列时候不同结果
print('x is a number of 3',sigmoid(3)) print('x is a array of [1,2,3]',sigmoid(np.array([1,2,3]))) 0utput:
x is a number of 3 0.9525741268224334
x is a array of [1,2,3] [0.73105858 0.88079708 0.95257413]
1.2 编写sigmoid_derivative方法实现sigmoid 梯度计算
sigmoid 的代价函数和推导过程可以看吴恩达老师的讲解,很好很详细。
我们直接引入代价函数。
补充一下sigmoid中对z的求导a*(1-a)的推导过程: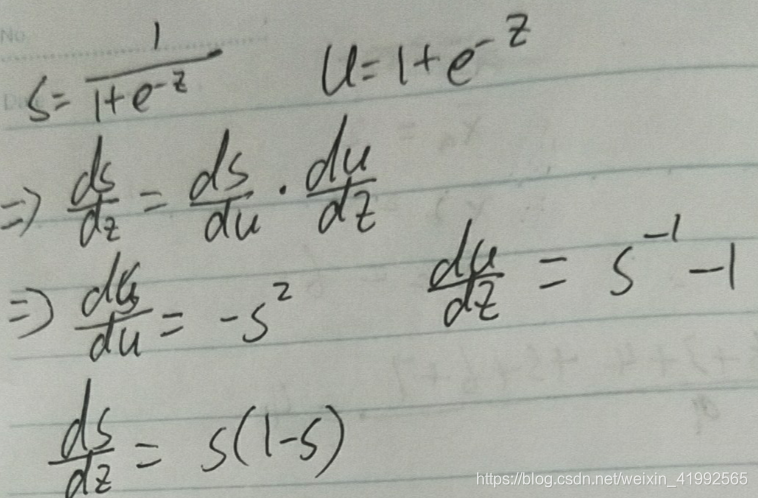
由上面公式得出对sigmoid求导
def sigmoid_derivative(x): s = 1/(1+1/np.exp(x)) ds = s*(1-s) return ds 1.3 引入猫的图片
开始练习矩阵的形状处理 ,这个图形其实可以理解成一个魔方。如果你了解图片rgb通道的话很容易就可以理解了。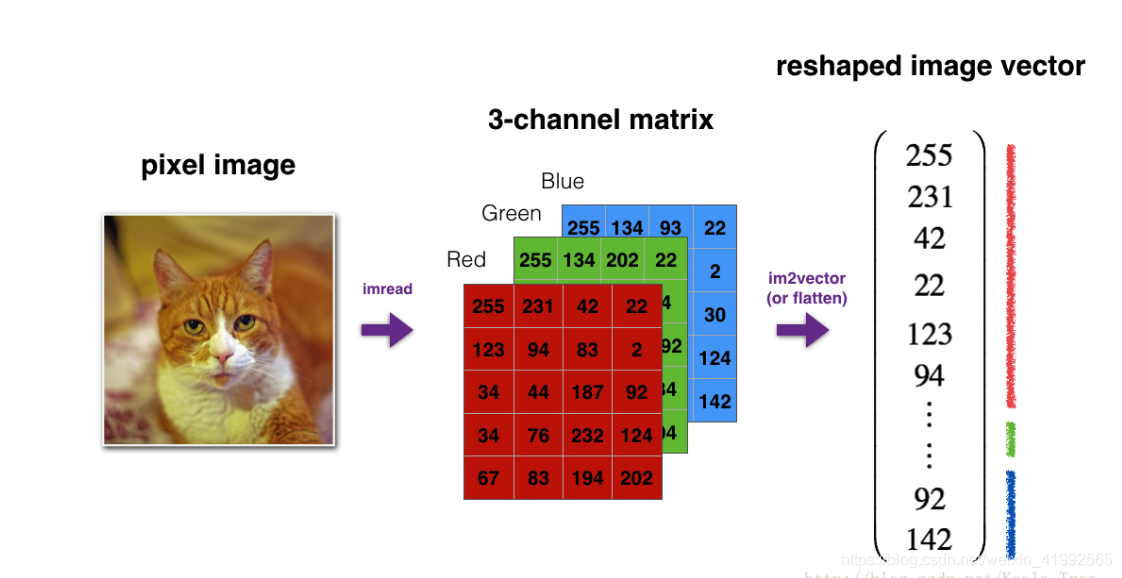
在没有涉及卷积网络的时候我们把矩阵处理成一维。
def image2vector(image): """ 把一个m*n*z 的图形矩阵变成 m*n*z 行 1列的矩阵 """ v = image.reshape((image.shape[0]*image.shape[1]*image.shape[2]),1) return v 测试一下:
image = np.array([[[ 0.67826139, 0.29380381], [ 0.90714982, 0.52835647], [ 0.4215251 , 0.45017551]], [[ 0.92814219, 0.96677647], [ 0.85304703, 0.52351845], [ 0.19981397, 0.27417313]], [[ 0.60659855, 0.00533165], [ 0.10820313, 0.49978937], [ 0.34144279, 0.94630077]]]) print ("image2vector(image) = " + str(image2vector(image))) output:
image2vector(image) = [[0.67826139]
[0.29380381]
[0.90714982]
[0.52835647]
[0.4215251 ]
[0.45017551]
[0.92814219]
[0.96677647]
[0.85304703]
[0.52351845]
[0.19981397]
[0.27417313]
[0.60659855]
[0.00533165]
[0.10820313]
[0.49978937]
[0.34144279]
[0.94630077]]
1.4 规范行
规范化就是矩阵除以矩阵的莫(范数),为了让梯度下降更快 例如矩阵的横向模(范数)=
def normalizeRows(x): #求出范数矩阵 x_norm = np.linalg.norm(x, axis=1, keepdims = True) #值除以范数 x = x / x_norm return x 测试一下:
x = np.array([ [0, 3, 4], [1, 6, 4]]) print("normalizeRows(x) = " + str(normalizeRows(x))) output:
normalizeRows(x) = [[0. 0.6 0.8 ]
[0.13736056 0.82416338 0.54944226]]
1.5广播和softmax功能
练习:使用numpy 实现softmax函数,你可以将softmax视为当你的算法需要更多类进行分类时使用的规范化函数(softmax 相当于一种特殊的sigmoid,适用于多分类)
def softmax(x): """ 计算输入x的每一行的softmax。 您的代码应该适用于行向量和形状矩阵(n, m)。 提要: x――形状的numpy矩阵(n,m) 返回: s――一个numpy矩阵,它等于(n,m)的softmax (x) """ #e的指数 x_exp = np.exp(x) #e的指数求和(这是个n*1)的矩阵 x_sum = np.sum(x_exp, axis = 1, keepdims = True) s = x_exp / x_sum return s 测试:
x = np.array([ [0, 3, 4], [1, 6, 4]]) softmax(x) output:
array([[0.01321289, 0.26538793, 0.72139918],
[0.00589975, 0.8756006 , 0.11849965]])
1.6 矢量化
在深度学习中,处理非常大数据集,确保代码具有计算效率所以需要使用矢量化
下面实现L1 L2的损失函数
def L1(yhat,y): loss = np.sum(np.abs(y-yhat)) return loss def L2(yhat, y): loss =np.sum(np.power((y - yhat), 2)) return loss